

Moreover, empagliflozin showed significant reduction in CV- and all-cause death in patients with T2DM with established CV disease. Additionally, empagliflozin, canagliflozin and dapagliflozin significantly reduced the HHF and the composite of CV death or HHF. Empagliflozin and canagliflozin have shown a significant reduction in composite of 3-point major cardiac adverse events (3P-MACE). Saxagliptin showed a significantly higher hospitalization due to heart failure (HHF).
TIMI TRIALS TRIAL
Nearly 8 years later, the more modern TACTICS-TIMI 18 trial has now reinvestigated the relative benefits of invasive vs conservative management and demonstrated that an early invasive strategy employed on top of a background of upstream tirofiban therapy was associated with improved clinical outcomes.Saxagliptin, alogliptin, sitagliptin and linagliptin are CV neutral drugs. This trial preceded the use of stents and glycoprotein 2b3a inhibitors as well as thienopyridines. Based on the absence of net clinical benefit, tPA is not recommended for routine use in patients with unstable angina or NQMI, such as those enrolled in this trial.įor early invasive compared with early conservative strategy, the groups did not differ in clinical outcome, although the early invasive strategy resulted in shorter initial hospitalization and rehospitalization rates. Nevertheless, intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 0.55% of TPA-treated patients. 32%, p < 0.001).Ī lower dose of tPA (average, 63 mg) was used in this trial compared with the usual dose used in the treatment of patients presenting with ST segment elevation and evolving Q-wave infarction. This result was related entirely to a small difference in angioplasty rates (39% vs. Revascularization by 1 year was common, but was slightly more common with the early invasive than the early conservative strategy (64% vs.

10.6%, p = 0.24).Īt 6 weeks, the principal end point for comparison of the two strategies occurred in 16.2% of the patients randomized to the early invasive strategy versus 18.1% of those assigned to the early conservative strategy (P=NS).Īverage length of initial hospitalization, incidence of rehospitalization within 6 weeks, and days of rehospitalization all were significantly lower (P<0.01) for the early invasive strategy.Īt 1 year, the incidence of death or nonfatal infarction was similar for the early invasive and early conservative strategies (10.8% vs. 4.9% P = 0.04).Īfter 1 year, the incidence of death or nonfatal infarction for the t-PA- and placebo-treated groups remained similar (12.4% vs. One third of the total dose but no more than 20mg was given ini Concomitant Medications:Īll patients were treated with bed rest, anti-ischemic medications, aspirin, and heparinĪt six weeks, an "unfavorable outcome" end point occurred in 54.2% of the tPA-treated patients and 55.5% of the placebo-treated patients (P=NS).īy 42 days the occurrence of MI was higher in patients receiving tPA than in patients receiving placebo (7.4% vs. The total dose of tPA or placebo was 0.8 mg/kg (maximum, 80mg). In a 2 x 2 factorial design, tPA or placebo as well as an early invasive or early conservative management strategy. Secondary Endpoints:ĭifferences in treatment effect (tPA versus placebo) or strategies (invasive versus conservative) for death or myocardial infarction for several subgroups. Previous coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)įor the comparison between tPA and placebo: "unfavorable outcome" at 6 weeks (death, postrandomization nonfatal myocardial infarction or reinfarction) or failure of initial therapyįor the comparison between the early invasive and early conservative strategies: death, postrandomization myocardial infarction, or an unsatisfactory ETT performed at 6 weeks. Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) within 6 months

Myocardial infarction within the preceding 21 days
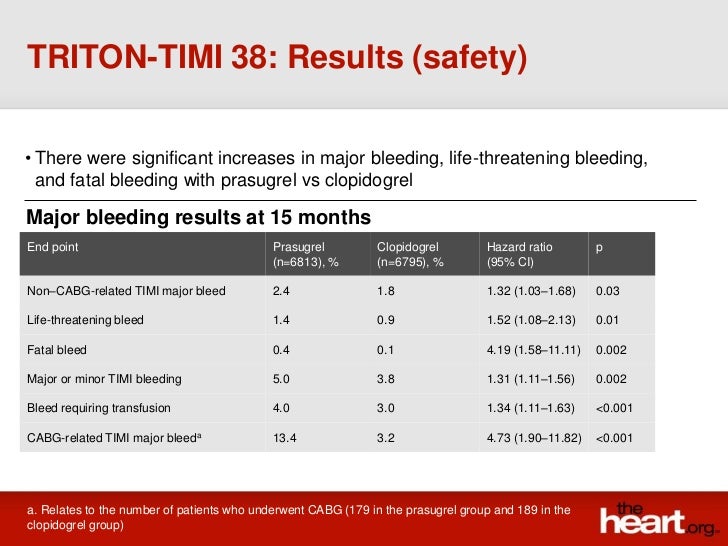
Objective evidence of ischemic heart disease by ECG in at least two contiguous leads (≥0.1-mV ST segment elevation lasting 180 mm Hg or a diastolic pressure >100 mm HgĬontraindication to thrombolytic therapy or heparin Chest discomfort at rest judged to be caused by ischemia, lasting ≥5 minutes but ≤6 hoursĭiscomfort must have occurred within 24 hours of enrollment


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
